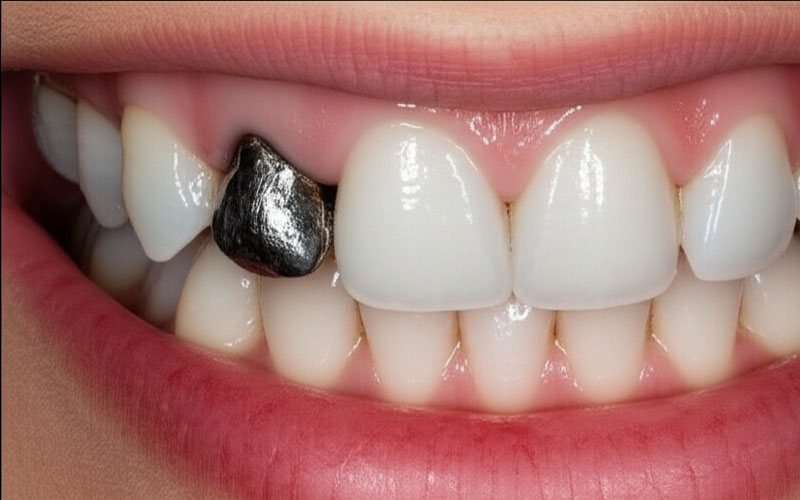
The Global Push for a Dental Amalgam Ban: Your Essential Guide to Mercury-Free Dentistry
Ever wondered what’s inside your dental fillings? Those silver-colored dental fillings—called “amalgam”—have patched up teeth for more than a hundred years. But now, people everywhere are asking: Are these fillings safe? Countries and dentists are starting to think about switching, and maybe you should too. Whether you’re a mom, a patient, or a dentist, this article will help you get what the dental amalgam ban means, why mercury matters, and what you can do about it. Let’s dig in and find out how to keep your smile safe and bright!
Table of Contents
What Is Dental Amalgam?
Dental amalgam is a material for fillings that dentists have used for about 150 years. It’s a mix of metals. Around half of it is mercury (that silver liquid that can be harmful), and the rest is silver, tin, copper, and zinc.
Dentists liked amalgam because it was tough. You could eat anything and it wouldn’t fall out, and it didn’t cost much. Insurance usually covered it too.
But there’s a catch. Mercury is part of amalgam, and that’s becoming a big worry worldwide.
Why Are People Worried About Dental Amalgam?
You’ve probably heard of mercury in science class. It’s a shiny liquid metal, but it’s not a friend if it gets into your body. Small bits of mercury can come out of fillings whenever you chew, brush your teeth, or drink something hot. That’s called mercury vapor.
That mercury can build up in your body. Over time, this can cause health issues.
This is why people get concerned. Mercury can damage the brain and kidneys, especially in children, women having a baby, or people who are already sick. Nobody wants a filling that could make them sick later on!
Thankfully, more dentists are moving to fillings without mercury. We’ll go through your choices in a bit.
Is Mercury in Dental Fillings Dangerous?
Let’s talk about what mercury does when it’s in your body. Mercury poisoning signs can sneak up and include:
- Forgetting things
- Trouble concentrating
- Strange muscle movements
- Always feeling tired
- Mood swings
Some doctors worry that mercury might be linked to diseases like multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, or even autism. Mercury doesn’t just disappear. It can get into your brain, kidneys, and nerves.
Experts still argue about how dangerous amalgam really is. Dentists say most grown-ups are probably okay—but it’s not good for everyone. FDA warnings say children under 15 and women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should pick fillings without mercury.
Here’s a simple table:
| Group | Should Avoid Amalgam? | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Children < 15 | Yes | Growing brains/kidneys |
| Pregnant women | Yes | Baby’s brain is growing |
| Nursing mothers | Yes | Mercury can be in breast milk |
| Kidney problems | Yes | Kidneys get rid of mercury |
| Healthy adults | Not clear | Less risk, but better choices exist |
What Does Dental Amalgam Do to the Environment?
Mercury doesn’t just stay in your mouth. Every time a dental office uses amalgam, some mercury can go down the drain and end up in the environment.
That waste doesn’t just vanish:
- It can get into rivers and lakes.
- Fish swallow mercury in the water.
- People eat the fish, and then the mercury gets into them.
Studies from the U.S. EPA say that dental offices are the biggest source of mercury in city waste water. That means animals and people everywhere can be at risk.
Dental mercury pollutes the planet.
People and animals—even far away—can be exposed to mercury from just a few dentist offices.
Green dentistry now uses amalgam separators and fillings without mercury to help stop pollution.
Which Countries Have Banned Dental Amalgam?
Some countries just decided it’s time to quit mercury fillings. Here’s a quick look:
| Country | Ban Start Date | Who Is Protected? |
|---|---|---|
| Norway | January 2008 | Everyone—all ages and groups |
| Sweden | June 2009 | Everyone—full ban |
| Denmark | January 2008 | Everyone, except rare health cases |
| European Union | July 2018 | Kids under 15, pregnant/nursing women |
| USA | No total ban | Strong waste rules, warnings for risk groups |
| Canada | No total ban | Warnings for kids, pregnant/nursing women |
Note: Most countries haven’t totally banned amalgam—yet. They’re stopping its use little by little, or keeping it away from people most at risk. More bans may come soon.
What Is the Minamata Convention on Mercury?
The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a really big international agreement. More than 140 countries signed it. It started on August 16, 2017. Its goal is simple: Use less mercury everywhere.
Article 4 of the treaty says countries should:
- Use less amalgam
- Try other kinds of fillings
- Stop using amalgam for kids and pregnant women, if possible
- Use safer dental methods
Mercury can travel around the globe, even if one country tries to keep it in.
If even one country keeps using a lot of mercury, it can hurt the whole planet.
If everyone works together, like the World Health Organization (WHO) wants, the world can get cleaner and safer.
What Are the Best Alternatives to Amalgam Fillings?
These days, you don’t need to worry about mercury. Fillings without mercury work just as well—and look better!
Composite Resins:
- Made from plastic and glass
- Look like a real tooth
- No mercury, good for most places in your mouth
- Used a lot now in the US, Canada, Europe
Porcelain or Ceramic Fillings:
- Best for big fillings or crowns
- Super strong, but cost more
- No metal, so many say they’re safer
Glass Ionomer Fillings:
- Stick to your tooth easily
- Good for kids, baby teeth, or small holes
- Release a little fluoride to keep your tooth healthy
| Material | Looks Like Tooth? | Mercury-Free? | Good for Big Holes? | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amalgam | No | No | Yes | Low |
| Composite Resin | Yes | Yes | Yes | Medium |
| Ceramic | Yes | Yes | Yes | High |
| Glass Ionomer | Yes | Yes | Not really | Low-Moderate |

Should I Get My Amalgam Fillings Removed?
So you might be asking: If I already have mercury fillings, do I need to take them out?
Experts say:
- If your fillings are healthy and you have no symptoms, leave them in.
- But if your fillings are broken, old, or you notice signs of mercury poisoning (like shaking, memory problems, health problems), see your dentist.
If you do want to take them out, make sure your dentist knows how to use the SMART Protocol. That stands for Safe Mercury Amalgam Removal Technique. It protects you and your dentist by:
- Using a rubber sheet and special suction
- Keeping the filling cool so less mercury vapor escapes
- Giving you clean air to breathe
Some holistic and biological dentists have extra training in this.
Mercury can leak out if you take fillings out the wrong way.
If a dentist removes your filling without being careful, you could breathe in more mercury than if you’d left it alone!
Always pick a dentist who follows SMART Protocol or other safe steps.
What Do Dentists Need to Know About Mercury Rules?
Dentists need to know and follow a lot of new rules!
- Amalgam Separators: Most US, European, and Canadian dental offices must use amalgam separators. This equipment stops mercury from getting into drains.
- Waste Rules: Dental offices must throw away mercury waste in a special way. Never in regular trash or drains.
- Learning: More dental schools now teach about composite, ceramic, and glass ionomer fillings. Old-school dentists get extra training, too.
Talking to Patients:
Dentists should always let you know all your choices. You have a right to hear the good and bad about every filling, so you can decide what’s best for you.
What Will Dental Fillings Look Like in the Future?
Dental fillings are only getting better with time!
New ideas:
- New composite resins last longer, look better, and stick really well
- Some fillings can fix themselves if they crack a bit
- Fillings are more gentle so they rarely cause allergies
Dental Trends:
- Focus on stopping cavities before they start
- Using sealants and fluoride to block decay
- Dentists and patients pushing for fillings that are safe, strong, AND good for nature
The future is mercury-free. Green dentistry is taking off, and the world is slowly moving away from dental amalgam.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it safe for kids to have mercury fillings?
No. Experts and the European Union say kids under 15 should get fillings without mercury whenever possible.
How do I find a dentist who uses mercury-free fillings?
Look for dentists that talk about “composite fillings,” “ceramic fillings,” “biological dentistry,” or “SMART Protocol.” Also check websites for the International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology (IAOMT).
Can I ask my insurance to pay for composite fillings?
Sometimes, yes. Lots of insurance now covers composite fillings. Ask your dentist to use the right codes when they submit your claim.
Can you be allergic to new filling materials?
It doesn’t happen often, but it’s possible. Tell your dentist about any allergies. They’ll help you pick the safest filling for you.
Important Things to Remember
- Dental amalgam (silver fillings) is about 50% mercury, which can cause problems.
- The mercury in fillings can harm your brain, kidneys, and more.
- Kids, pregnant women, and nursing moms should not get mercury fillings.
- Many countries are stopping or banning dental amalgam; the Minamata Convention makes rules for the whole world.
- Composite, ceramic, and glass ionomer fillings are good mercury-free choices.
- Never take out amalgam yourself—use the SMART Protocol to stay safe.
- Dentists have to handle mercury waste carefully and use safe filling methods—it’s the law.
- Filling materials keep getting better, making dental work safer and more natural-looking.
- Always talk with your dentist about what’s best for YOU and your health.
Keep learning. Take care of your teeth. Choose smart dentistry for a safer, happier smile!